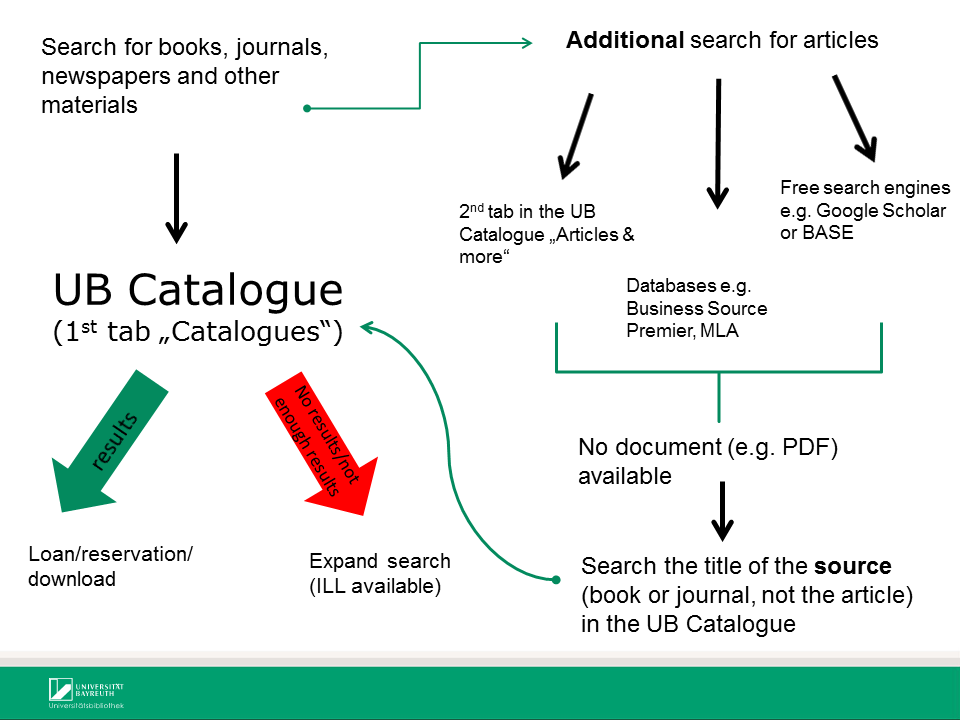
Before starting your literature search, identify appropriate search terms for your topic. You can find them e.g. in dictionaries, encyclopedias or lexica. Textbooks can provide alternative perspectives and more detailed information on your search topic.
Sample collection of search terms for the topic "Internal communication in small businesses"
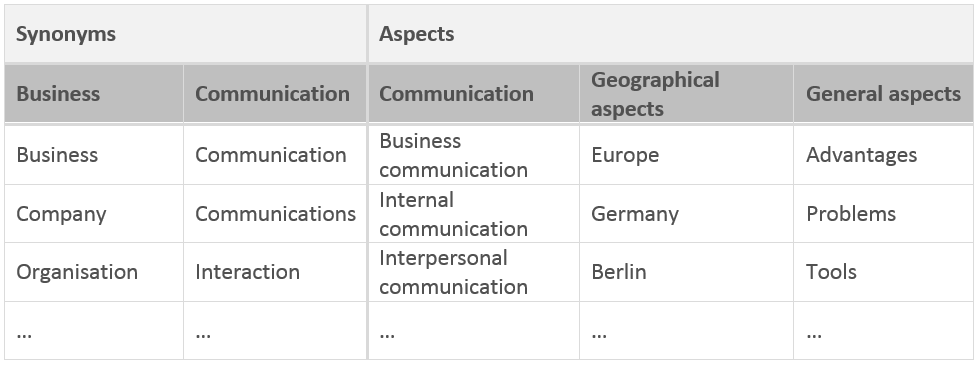
How to find search terms:
- Include terms in different languages (Most databases record publications in English).
- Include different spellings.
- Include singular and plural forms.
- Consider subject jargon and colloquial language/terms (Use special thesauri, e.g. the Thesaurus of Economics).